Businesses are adopting the cloud as the cloud introduces some new business capabilities and benefits. It offers businesses the capability to scale their resources dynamically. With this benefit, it will be simpler for any organisation to adapt to the changing demands and efficiently manage its infrastructure. Therefore it is wise to choose the right managed cloud for any business.
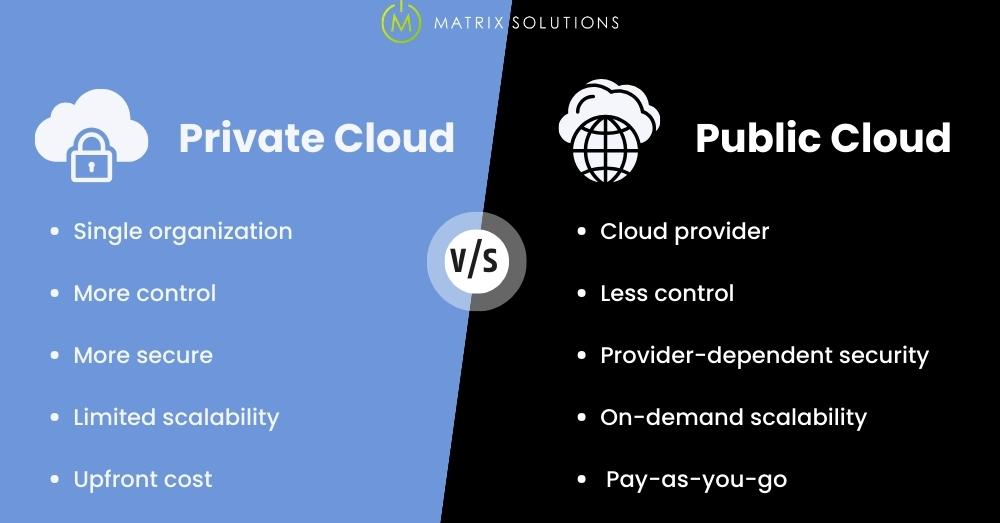
Organisations use shared cloud infrastructure in a public cloud, while in a private cloud, they use their own infrastructure. A private cloud may require a higher upfront investment than public clouds and provide more control, customisation, and security for businesses’ critical applications and data.
So, what are these two cloud solutions, and what factors do we need to consider when choosing between private and public cloud?
What are Private and Public Clouds?
Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment exclusively dedicated to a single organisation or business. It caters to a single organisation, offering enhanced security and control over resources and data privacy.
Organisations often choose private clouds that handle sensitive data, have regulatory compliance requirements, or demand more control over their infrastructure.
Public Cloud
A public cloud provides services over the Internet, allowing multiple organisations to share the same infrastructure. Third-party providers manage it and offer scalability and cost-effectiveness. Cost reduction is one potential benefit.
Popular public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud. These platforms offer various services, such as virtual machines, storage, databases, machine learning, and more. It enables organisations to build and deploy applications without investing heavily in hardware and infrastructure.
Similarities Between Private and Public Cloud
Private cloud and public cloud share some common features and benefits. Both types of clouds also offer the advantage of easy scalability, allowing businesses to quickly adjust their computing resources based on demand. Moreover, they provide remote accessibility, enabling users to access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. Some more key points highlighting the similarities between private and public cloud are:
- Cost flexibility
- High availability
- Vendor Support
- Disaster recovery
- Security measures
Also, find the differences between private cloud and public cloud below:
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud
|
Aspect |
Private Cloud |
Public Cloud |
|
Costs |
Needs higher upfront investment in hardware and ongoing maintenance |
Needs lower upfront costs, as infrastructure is shared among multiple clients |
|
Location |
Can be deployed within the organisation’s data centers |
Can be maanaged and hosted by a third-party cloud service provider |
|
Infrastructure |
The organisation owns and manages the hardware and infrastructure |
Third-party provider owns and manages the hardware and infrastructure |
|
Maintenance |
Responsible for all maintenance, upgrades, and security patches |
Maintenance, upgrades, and security managed by the service provider |
|
Security |
Provides higher control over security measures and compliance |
Security measures implemented by the service provider may vary |
|
Scalability |
Scalability depends on the capacity of the on-premises infrastructure |
Easily scalable, resources can be adjusted based on demand |
|
Expertise Required |
Requires in-house IT expertise to manage the cloud environment |
Requires less in-house expertise, as the provider manages the infrastructure |
|
Flexibility |
Offers greater flexibility in tailoring the cloud environment to specific needs |
May have some limitations on customisation due to shared infrastructure |
|
Connectivity |
It may require dedicated and secure network connections |
Accessible over the internet with secure connectivity options |
Key Considerations of Managed Cloud Services
Managed cloud services bring additional benefits to both private and public cloud environments. Managed public cloud services are handled by experienced cloud service providers. They offer;
- 24/7 monitoring and support for enhanced reliability.
- Regular updates and maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
- Scalability to meet changing business needs efficiently.
- Maximum control and customisation over the cloud environment
- Flexible pricing, i.e., pay for the resources you use.
Managed Private Cloud
Managed private cloud services provide specialised support and benefits, including:
- Improved security measures through proactive threat monitoring.
- Ensure compliance with relevant data protection and privacy standards.
By carefully considering the advantages of managed cloud services for private and public cloud options, you can make an informed decision aligning with business goals and IT requirements. Whether you opt for a managed public cloud for cost-effective scalability or a managed private cloud for enhanced security and control, partnering with the right cloud service provider. They will benefit you in unlocking the full potential of cloud computing for your organisations.
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud
Choosing between private cloud and public cloud is one critical decision. Considering the following (points) can help you determine the best side and help your business to reach new heights.
Security and Compliance
Security is a primary concern for organisational firms.
Private Cloud Security:
- Offers dedicated firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems for maximum protection.
- Enables easier compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Public Cloud Security:
- Utilises robust security measures, such as data encryption and access controls, but it’s shared across multiple clients.
- May require additional security layers for sensitive legal data.
Cost Comparison
Cost is crucial when deciding between private and public clouds.
Private Cloud Costs:
- Higher initial setup costs due to dedicated infrastructure and equipment.
- Predictable monthly expenses with fewer variable costs.
Public Cloud Costs:
- Lower upfront investment with pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Cost fluctuations based on resource usage are potentially higher in the long term.
Control Over Resources and Data Privacy
Data sovereignty and resource control are vital concerns.
Private Cloud Control:
- Complete control over data location, ensuring compliance with local data regulations.
- Customisable resource allocation based on specific requirements.
Public Cloud Control:
- Limited control over data location and infrastructure, as it is shared with other clients.
- Standardised resource allocation based on the cloud provider’s offerings.
Besides private and public clouds, many organisations are now using a hybrid cloud model, which combines elements of both clouds. This approach combines each type’s advantages and disadvantages to create a unified IT environment.
As we conclude, what matters most is making the right choice for your business. Select the solution that best aligns with your specific needs.
Private Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: Differences
The process of hybrid cloud deployment combines private and public cloud services to create a unified infrastructure.
The key difference between a private cloud and a hybrid cloud lies in their architecture and resource allocation. A private cloud provides enhanced control and security to a single organisation as all infrastructure and data reside on a private network.
But, a hybrid cloud combines the features of both private and public clouds, allowing businesses to leverage both benefits. It integrates on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, enabling seamless data and application migration between environments.
While a private cloud offers greater customisation and data privacy, a hybrid cloud presents more flexibility, cost-efficiency, and the ability to scale computing resources based on demand, making it suitable for organisations with varying workloads and data sensitivity.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Industry
In conclusion, choosing between private and public clouds depends on your business’s unique needs and preferences. A private cloud might be more suitable if data security and control are top priorities. On the other hand, a public cloud is an attractive option if cost-efficiency and scalability are critical.
Consulting with a managed cloud service provider, like Matrix Solutions, can provide you with fair and comprehensive advice on the best setup for your business. They offer managed IT services, including managed cloud services, to ensure you understand not only the costs and benefits but also the impact on your work processes and organisational use. With Matrix Solutions, you’ll gain insights into how both cloud platforms can enhance your operations and unlock future opportunities, helping your business thrive in a dynamic digital landscape.
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud FAQs
Is public cloud better than private cloud?
The answer depends on your business requirements. Public clouds offer cost-effectiveness and scalability, while private clouds prioritise security and control.
What are the examples of private cloud?
Private cloud providers include Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Dell, IBM, Oracle, and some familiar names from the public cloud provider space, including AWS, Google, and Microsoft.
Who should use private cloud?
Organisations dealing with sensitive data, such as legal firms, healthcare providers, or financial institutions, can benefit from the security and customisation a private cloud offers.
What is the major drawback of public cloud?
Due to shared resources, public clouds potentially lack control over data and security configurations.
Is private cloud safer than public cloud?
Private clouds are generally considered safer due to their dedicated resources and personalised security measures. However, public clouds can also be secure with proper configurations and additional security layers.
What is hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a computing model that allows the organisation to run a workload in the optimal environment and shift that workload based on capacity, demand or costs.